13 Types of Digital Designers
Categories
Pro Tips
Business
Other
Author
Lee Barguss
Published
24 Oct 2022

Digital designers come in all shapes and sizes. Long gone are the days when you could hire a graphic designer or illustrator to get any job done that you can think of since the digital world has become much more massive, complicated and full of things.
Looking to hire a digital designer to help with your project, but not sure what type you need? A lot of different types of digital designers have overlapping skills that are used across different industries and applications, but with the complexity of modern products and marketing, it’s now very common to have a specialist involved in the design process.
Here is a handy guide that outlines all the different types you can come across, their specialities and what tools they use for their craft. Tap on any of these to skip down the list:
Animation Designer
Art and Illustration Designer
Experiential Designer
Front-End Designer
Game Designer
Graphic Designer
Industrial Designer
Information Designer
Motion Designer
Product Designer
User Experience (UX) Designer
User Interface (UI) Designer
Web Designer
Video source: Kurzgesagt – In a Nutshell
Animation Designer
Animators concentrate on the art form of cinematic effects and storytelling techniques to craft a narrative. They create both 2D and 3D moving images and effects for a wide range of formats such as video games, websites, mobile apps, tv shows, movies, and adverts. Animators are not necessarily limited to just digital, but the field includes any moving image from hand-drawn cartoons to clay stop-motion.
Tools commonly used by (digital) animation designers include:
3D Studio Max
Adobe CC (After Effects and Illustrator)
Cinema 4D

Image source: Pickle Illustration
Art and Illustration Designer
More commonly known as an illustrator, these designers create visual ways to convey written information that can be found on book covers, posters and flyers, educational materials, adverts and magazines. Illustrators will use a mixture of both traditional and digital tools to create their designs.
Tools commonly used by illustrators include:
Pencils, pencils, inks, paints
Adobe CC (Photoshop and Illustrator)
Corel
Procreate

Image source: Museum of Illusions, Zagreb
Experiential Designer
Much like an information designer (further down the page), an experiential designer creates information systems but for the physical space in order to communicate a particular message or feeling. These designers are used to build physical marketing campaigns, art exhibitions and public installations, and turn them into experiences.
Tools commonly used by experiential designers include:
Adobe Photoshop
ClickUp
Figma
Miro

Image source: Ilya Pavlov
Front-End Designer
Also known as front-end developers, these designers are responsible for coding designs of websites and web apps to life using languages such as HTML, CSS, C++, DOM and Javascript. They will ensure that the sites are ready for live viewing in a variety of different screen sizes, operating systems and web browsers.
Tools commonly used by front-end designers include:
AngularJS
CodePen
jQuery
GitHub
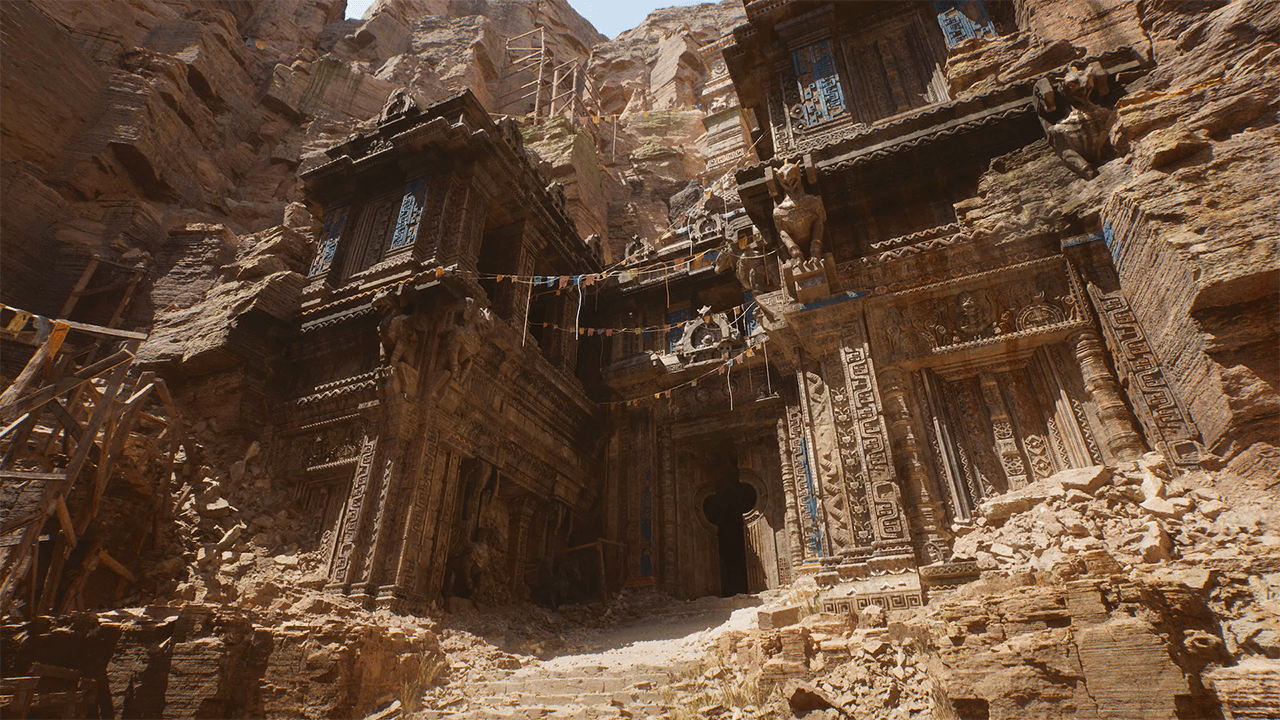
Image source: Unreal Engine 5
Game Designer
A rather broad addition to this list, but an important one at that. A game designer will have expertise in a variety of skills, including the layout, code, storyline, environment, characters, and sounds of video games. Because of their valued skill set, they can also be used to create immersive experiences for users in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), 3D audio and cinematic experiences in large environments.
Tools commonly used by game designers include:
Maya
Nuke
Unreal Engine
ZBrush

Image source: Jordan Jenkins
Graphic Designer
These designers are probably the most common type of designers out there – they use visual elements such as colour, image and typography to communicate information in a visual way. Graphic designers will have experience in both digital and print formats, so they’re a valuable asset when creating a brand / visual identity. They can convert a company’s characteristics and values into a meaningful form and expand that into targeted messaging (brand collateral) used to support sales and marketing.
Tools commonly used by graphic designers include:
Adobe CC (Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign)
Affinity
Corel
GIMP
Image source: Version 22
Industrial Designer
An industrial designer is someone who designs physical products, combining both engineering and business/market knowledge. They will be able to design and develop products in the auto, toy, sports, home, kitchen and medical industries, being able to design for form, function, production and manufacturing.
Tools commonly used by industrial designers include:
Adobe Illustrator
AutoCAD
KeyShot
Solidworks
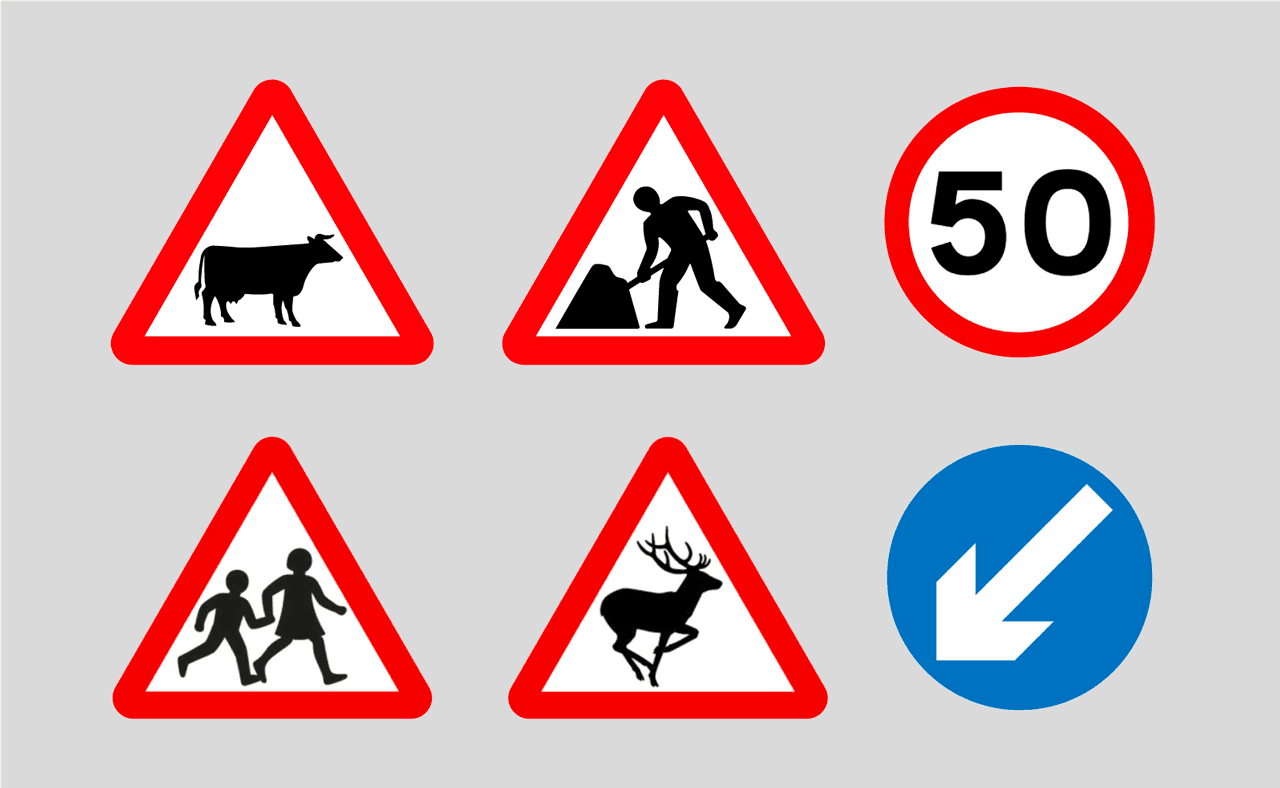
Image source: Margaret Calvert
Information Designer
Information designers study, collate and translate data into intuitive information systems with the purpose to create reactions in the user. In other words, they are analytical storytellers that use imagery, colour, shape, texture and type to communicate information and feelings in a specific order and structure. Designs created in this field can be anything from infographics to road signs.
Tools commonly used by information designers include:
Adobe CC (Illustrator, InDesign and Photoshop
ClickUp
Figma
Miro

Motion Designer
These kinds of designers are a more specific type of animators that are usually specialised in shapes, objects or text being set in motion. Motion designers work in the same field as animators but usually work in digital 2D moving imagery, giving life to graphical elements, usually without following any specific narrative.
Tools commonly used by motion designers include:
3D Studio Max
Adobe CC (After Effects and Illustrator)
Cinema 4D
Red Giant Software

Image source: Nirmal Rajendharkumar
Product Designer
Product designers combine the skills of a UI designer and a marketer to create a cohesive relationship between end-user expectations and brand strategy in their designs. They’re usually somebody who oversees the whole design process of a product from start to finish or the improvement of an existing product through ideation and conceptualisation. Their skills include familiarity with UI and UX design, product management tools, and front-end coding so they can communicate their plans.
Tools commonly used by product designers include:
Adobe XD
Figma
InVision
Marvel POP
Sketch
Image source: Michal Kulesza
User Experience (UX) Designer
UX designers directly inform other digital designers’ processes with their research about users’ needs, behaviours and motivations. They identify problems and create beneficial solutions that are goal-oriented. UX designers will often work with UI designers to create user journeys and flows, and can even create wireframe designs to instruct more high-level designs.
Tools commonly used by UX designers include:
Adobe Xd
Figma
InVision

Image source: TawfiQul Emon
User Interface (UI) Designer
UI designers are responsible specifically for the visuals and styling of websites and mobile applications. They’ll always be very familiar with UX (user experience) and therefore apply it to their work, but a serious (and large) product build will always have UI and UX designers partner and work closely together. UI designers wireframe, create design systems, prototype and test their designs.
Tools commonly used by UI designers include:
Adobe CC (Photoshop, Illustrator, Xd)
Affinity
Figma
Sketch

Image source: Musemind Agency
Web Designer
Web designers essentially create online “home bases” for business – anything from a simple landing page to outline key features to a fully decked-out eCommerce site. They are responsible for translating a brand’s brand collateral into a structured format that conveys a large sum of information to readers and potential customers. Web designers balance usability with aesthetics in their design process and will have expertise in both UI (user interface) and UX (user experience). They don’t necessarily know how to code a website (that’s up to a web or front-end developer), but they’ll usually be familiar with HTML, CSS and Javascript.
Tools commonly used by UX designers include:
Adobe CC (Photoshop, Xd)
Figma
Squarespace
Wix
WordPress